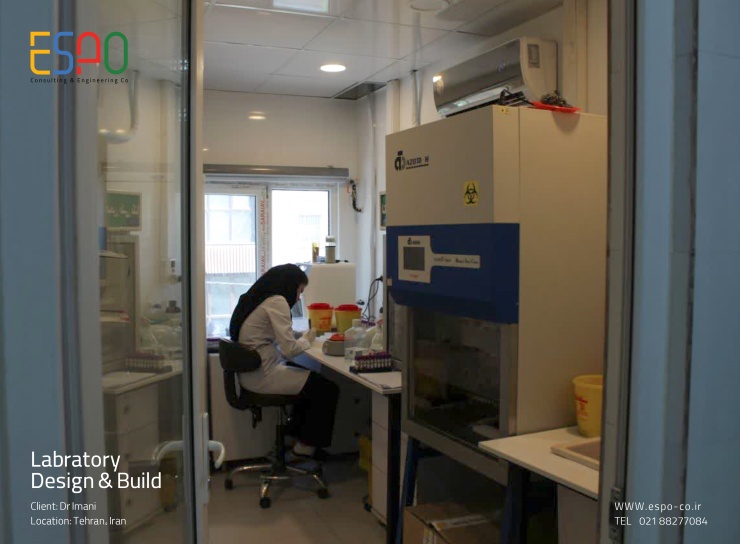
The design of a medical diagnosis laboratory requires attention to several key factors, including health standards, ergonomics, work flow, safety and productivity. In the following, important principles and points that should be considered in the design of a medical diagnostic laboratory are presented:
Principles of medical diagnosis laboratory design
1. Space layout and design:
Division of spaces: The laboratory should be divided into different sections such as reception and waiting, sampling section, sample preparation section, analysis section (biochemistry, hematology, microbiology, etc.), storage rooms and reporting section.
Optimal workflow: The design of spaces should be such that the workflow from sample collection to analysis and reporting is done smoothly and without interference. This helps to reduce the risks of cross-contamination and increase productivity.
2. Ventilation and air quality control:
Proper ventilation system: Medical diagnostic laboratories need air conditioning systems and HEPA filters to prevent contamination and maintain air quality. The ventilation system should be such that clean air enters and contaminated air is directed outside.
Humidity and temperature control: Maintaining proper temperature and humidity control is essential for the stability of samples and the performance of sensitive devices.
3. Selection of equipment and furniture:
Efficient and up-to-date equipment: The choice of laboratory equipment such as centrifuges, automatic analyzers, and refrigerators should be based on the type of tests performed and the specific needs of the laboratory.
Furniture and desks of the right material: Desks and cabinets should be made of materials that are resistant to chemicals and pollution (such as stainless steel).
4. Safety and health:
Disinfectants and hand washing stations: Disinfectants, washing sinks and hand washing stations for employees should be available in various locations.
Emergency exit routes and safety equipment: Installation of alarms, emergency exit routes, fire extinguishers and emergency showers are essential for emergencies.
5. Lighting and acoustics:
Adequate lighting: Natural and artificial light should be combined in such a way that sufficient illumination is provided for the accuracy of the experiments. Lighting with appropriate intensity and temperature is required to reduce eye fatigue of employees.
Sound and acoustic control: Laboratory environments should be designed in such a way that excess noise is reduced and staff concentration is maintained.
6. Data and information management systems:
Communication networks and data management software: There should be a robust IT infrastructure that supports accurate recording and storage of test data and enables data transfer to medical systems.
7. Accessibility and ergonomics:
Easy access: The design should provide easy and convenient access to equipment and work spaces for employees. Good ergonomics in the design of furniture and work space is necessary to reduce physical injuries of employees.
The medical diagnostic laboratory includes different departments, each of which has specific tasks for performing diagnostic tests and analyses. These departments are designed to ensure efficient workflow, safety, and quality control. In the following, the different parts of the medical diagnosis laboratory and the duties of each part have been introduced:
1. Information acceptance and registration department:
Duties: Record patient information, accept samples, and issue identification codes for each sample.
Features: This department should be connected to laboratory information management systems (LIMS) and data recording software.
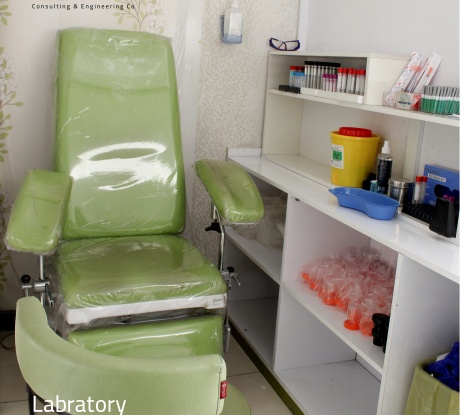
2. Sampling department (Phlebotomy Room):
Duties: Collect blood, urine, saliva, and other samples from patients.
Features: Must have sample collection stations, comfortable seating for patients, and disinfection equipment. Also, it should have a proper ventilation system to maintain the safety of employees and patients.
3. Sample Preparation Area:
Task: Initial preparation of samples for analysis. This may include centrifugation, pipetting, dilution, and other preparation processes.
Features: It has various equipment including centrifuges, safety hoods, and refrigerators for storing samples.
4. Department of Biochemistry:
Task: Perform various biochemical tests such as measuring blood sugar, cholesterol, enzymes, and electrolytes.
Features: Equipped with automatic biochemistry analyzers, special refrigerators and freezers to store reagents and samples.
5. Hematology department:
Duties: Perform hematology-related tests such as blood cell counts, coagulation tests, and blood grouping.
Features: Equipped with automated hematology analyzers, microscopes, and personal safety equipment.
6. Department of Microbiology:
Task: Cultivating and identifying microorganisms from various samples (such as urine, blood, and wounds) and performing antibiotic sensitivity tests.
Features: with incubators, autoclaves, biological safety hoods, and special spaces for the cultivation and growth of microorganisms.
7. Department of Immunology and Serology:
Duties: Perform tests related to the immune system such as measurement of antibodies and antigens, ELISA tests and other related diagnostic tests.
Features: equipped with immunology analyzers, refrigerators for storing reagents, and precision instruments such as pipettes.
8. Department of Hormonology (Hormone Assay):
Task: To measure the levels of various hormones in the body using techniques such as radioimmunoassay (RIA) or ELISA.
Features: It has accurate equipment for measuring hormones, special refrigerators and ELISA devices.
9. Department of Molecular Diagnostics:
Task: Perform molecular tests such as PCR to identify infections, genetic disorders and DNA/RNA analysis.
Features: Equipped with PCR machines, DNA and RNA extraction systems, and safety hoods to prevent contamination.
10. Reagent and Sample Storage section:
Duties: Maintain reagents, kits, and chemicals required for conducting experiments.
Features: Includes refrigerators, freezers, and special cabinets with proper ventilation.
11. Washing and Sterilization Area:
Task: washing and disinfecting laboratory equipment, containers and instruments.
Features: Large sinks, autoclaves and disinfection equipment.
12. Reporting and Data Management department:
Task: Analyzing the results, preparing diagnostic reports and sending the results to doctors and patients.
Features: computer systems and laboratory information management software (LIMS) for data processing and reporting.
13. Administrative and Support Area:
Duties: Overall laboratory management, customer service, and administrative duties.
Features: Administrative offices, meeting rooms, and support spaces such as staff break rooms.
Conclusion:
Each part of the medical diagnostic laboratory must be carefully designed to ensure safety, efficiency and accuracy in performing tests. The right combination of modern equipment, suitable work space and health and safety standards are the basic foundations of a successful laboratory.